The rapid adoption of SaaS applications has revolutionized how businesses operate, offering flexibility and scalability. However, as data and operations migrate to the cloud, security has become a critical concern.
Cloud security in SaaS involves protecting applications, data, and users from growing threats. This guide provides a beginner-friendly overview of cloud security in SaaS applications, including its principles, challenges, and best practices.
What is Cloud Security in SaaS?
Cloud security in SaaS refers to the measures and technologies designed to safeguard cloud-based applications and the sensitive data they manage. SaaS applications run on cloud infrastructures, requiring strong security measures to guard against breaches, unauthorized access, and cyber threats.
These measures ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, making cloud security a cornerstone of successful SaaS deployments.
Key Threats and Risks in SaaS Cloud Environments

Data Breaches
Data breaches are a significant threat to SaaS cloud environments, often resulting in the exposure of sensitive customer or business information. These breaches can cause severe financial losses, legal fallout, and long-term reputational damage.
Causes of Data Breaches
- Weak Access Controls: Poorly managed permissions or weak passwords can allow unauthorized individuals to access sensitive information.
- Cloud Misconfigurations: Incorrectly configured storage or security settings in cloud environments create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals use deceptive emails or messages to steal login credentials, enabling access to critical systems.
Insider Threats
Insider threats happen when someone within an organization, knowingly or unknowingly, compromises security. These risks are particularly challenging to detect as insiders already have access to critical systems.
Types of Insider Threats
- Malicious Insiders: Employees or contractors who exploit their access to benefit themselves or damage the organization.
- Negligent Insiders: Individuals who unintentionally create vulnerabilities by failing to follow security protocols, such as sharing passwords or mishandling data.
- Third-Party Insiders: External vendors or partners with access to systems who may negligently or intentionally expose sensitive information.
Ransomware and Malware Attacks
Ransomware and malware attacks are among the most disruptive threats to SaaS applications. These attacks often involve encrypting critical data or stealing sensitive information, forcing organizations to pay a ransom or face operational downtime.
Types of Ransomware and Malware Attacks
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Outdated software or unpatched systems provide entry points for attackers.
- Social Engineering: Tactics like phishing trick employees into downloading malware or providing access credentials.
- Compromised Third-Party Tools: Integrations with unsecured third-party software can introduce vulnerabilities into the system.
By combining real-time alerts with a business intelligence platform can uncover hidden security gaps and patterns. Therefore, we can mitigate the key threats and risks in saas cloud environment.
Core Principles of Cloud Security
Confidentiality
Confidentiality, a key principle of cloud security, ensures that sensitive information is available only to authorized users. Protecting information from unauthorized access involves implementing strong encryption methods, role-based access controls, and secure communication protocols.
Integrity
Integrity ensures data remains accurate, consistent, and free from unauthorized alterations throughout its lifecycle. This principle is vital for maintaining the reliability of SaaS applications. Verification mechanisms, such as digital signatures or hash functions, help detect any unauthorized changes to files or data records.
Availability
Availability guarantees that SaaS applications and their data are accessible whenever users need them. This principle relies on robust infrastructure, including disaster recovery plans, redundant systems, and real-time uptime monitoring.
Accountability
Accountability involves ensuring that every action within a SaaS environment is traceable to a specific user or process. Implementing detailed logging and monitoring systems helps track access, modifications, and other activities within the system.
Non-Repudiation
Non-repudiation ensures that individuals cannot deny their actions, such as making changes to data or completing transactions. This principle is essential for maintaining accountability and meeting compliance requirements.
Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential security threats to SaaS applications. Organizations must regularly evaluate their cloud environments for vulnerabilities and implement strategies to minimize risks.
This includes conducting penetration testing, using security frameworks like NIST or ISO 27001, and continuously updating threat models to address emerging risks.
Essential Security Features for SaaS Applications
Data Encryption
Data encryption safeguards information while it is being transferred or stored, preventing unauthorized access. Strong encryption standards protect sensitive business and customer data.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM systems manage user permissions, ensuring that access to specific resources is restricted to authorized individuals only.
Continuous Monitoring
Real-time monitoring identifies potential threats and vulnerabilities before they escalate. Alerts and reports enable quick responses to security issues.
Best Practices for SaaS Cloud Security

Limit Access with Role-Based Controls
Implementing role-based access controls (RBAC) ensures users can only access the data and resources necessary for their tasks. This minimizes exposure of sensitive information and reduces the risk of accidental or malicious actions.
Integrate Real-Time Threat Detection
Using tools with real-time threat detection capabilities helps identify and neutralize potential risks before they escalate. These systems monitor network activity, flagging unusual behavior that may indicate a breach.
Educate Users About Security Protocols
Training users on security best practices helps prevent common errors that lead to vulnerabilities. Use a learning management system to train staff on phishing threats and safe data handling. It should address topics like spotting phishing scams, using strong passwords and avoiding suspicious links.
Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encrypt sensitive data by converting it into an unreadable format, to ensure its safety during transmission and storage. This protective measure prevents unauthorized access to critical data.
Automate Patch Management
Automated patch management tools keep software and systems updated with the latest security patches, minimizing the chances of vulnerabilities being exploited.
Conduct Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Scans
Regular penetration testing helps uncover vulnerabilities in SaaS systems that attackers could exploit. Pairing this with vulnerability scans allows organizations to detect and resolve risks early.
Establish Incident Response Procedures
A well-defined incident response plan enables teams to respond quickly during a security breach. The plan should include detailed steps for detecting, containing, and addressing threats while reducing operational disruptions. A SaaS helpdesk centralizes support tickets and speeds up responses during potential security breaches.
Monitor User Activity
Continuous user activity monitoring helps detect unauthorized access or unusual behavior. Tools like user behavior analytics (UBA) identify deviations from normal patterns, enabling faster responses to potential threats.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA increases protection by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple authentication methods before access is granted. Even if credentials are compromised, MFA significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized entry. It is a cost-effective and reliable method to strengthen SaaS security.
Perform Regular Security Assessments
Regular security assessments help identify gaps in existing measures and provide actionable recommendations for improvement. These assessments evaluate the effectiveness of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and overall security posture.
Common Challenges in Implementing Cloud Security
Balancing Security and Usability
Overly strict security measures can affect user experience, while minimal measures increase risks. Finding the right balance is essential.
Adapting to Evolving Threats
Cyber threats are constantly increasing, with attackers using advanced techniques to exploit vulnerabilities. To stay protected, organizations need to regularly update their security tools and patch systems and adopt the latest threat detection technologies.
Managing Shared Responsibility
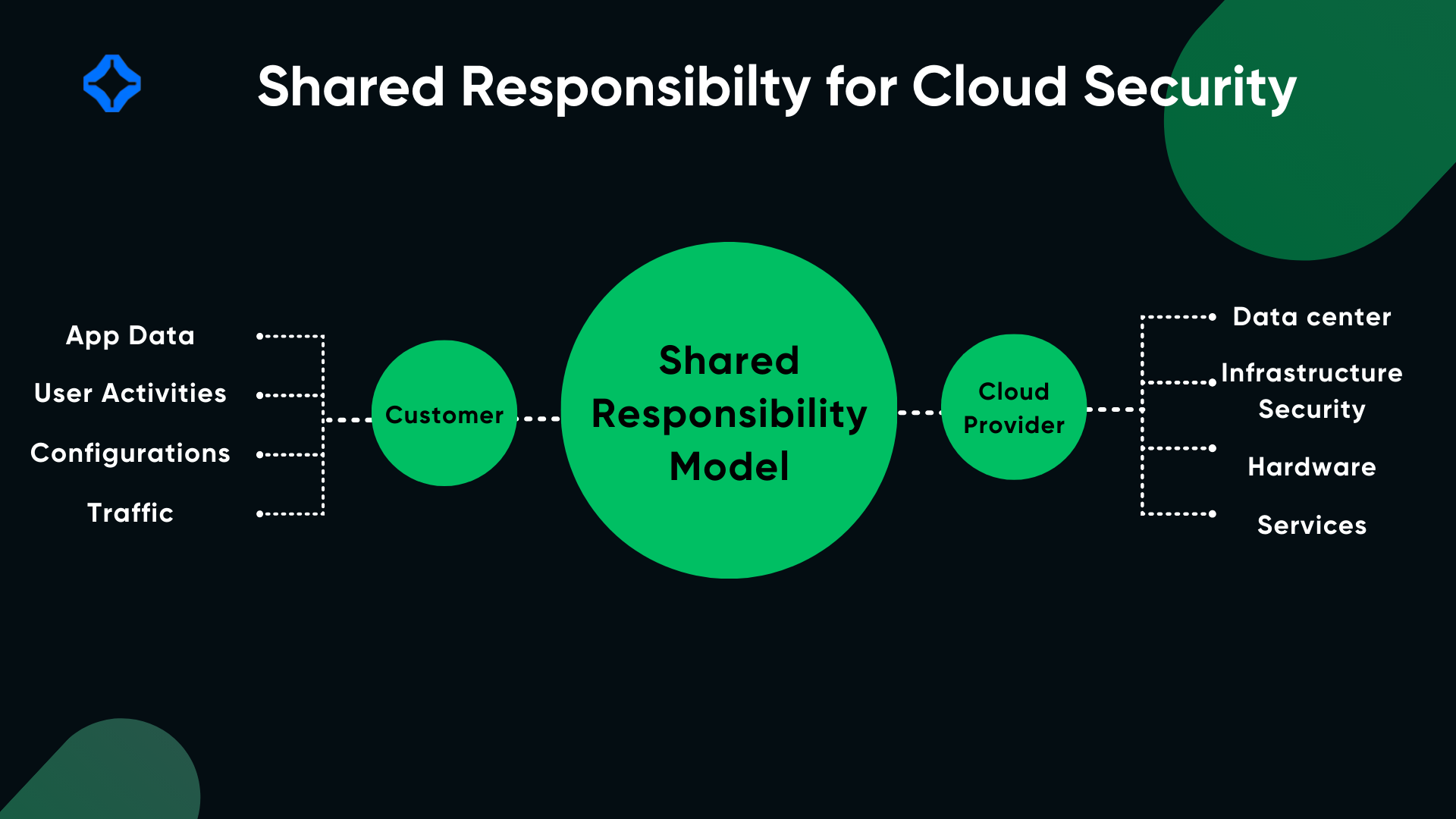
In SaaS environments, the service provider and the user share security responsibilities. Providers handle infrastructure security, while users are responsible for securing data, user access, and configurations.
Tools and Technologies for Strengthening SaaS Security
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
CASBs serve as a bridge between users and cloud service providers, providing oversight and management of cloud service activities. These tools implement security policies like data loss prevention (DLP) and detect shadow IT activities involving unauthorized app usage.
CASBs also support compliance by ensuring data handling aligns with industry regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. With CASBs, organizations can protect sensitive information while maintaining productivity in cloud environments.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR solutions protect endpoints, such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices, that access SaaS applications. These tools continuously monitor endpoint activities, identifying and responding to threats in real time.
EDR systems can detect advanced threats, such as fileless malware or zero-day attacks, that traditional antivirus programs may miss
Encryption Tools
Encryption tools are essential for safeguarding sensitive data throughout its lifecycle in SaaS applications. These tools keep data safe during transfer and storage by transforming it into encoded formats accessible only through decryption keys.
Advanced encryption methods, such as AES-256, provide strong protection against unauthorized access or tampering. Regularly updating and auditing encryption methods ensures they remain effective against future threats.
The Role of Compliance and Regulations in SaaS Security
Following regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 is vital for SaaS providers to gain and maintain customer trust. These regulations establish clear protocols for handling and protecting sensitive data, ensuring organizations follow industry best practices.
To maintain compliance, organizations should continuously monitor regulatory changes and update their practices accordingly. Staying updated in this area ensures legal adherence and reinforces trust with customers and stakeholders.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Security for SaaS
AI and Machine Learning
AI-driven automation tools are revolutionizing SaaS security by detecting threats faster and automating responses. Machine learning strengthens threat detection by analyzing patterns and anomalies.
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust principles minimize risks by requiring verification for every access request, regardless of location or user.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
SASE combines network security and wide-area networking (WAN) to provide comprehensive protection for SaaS applications and remote users.
Conclusion
Cloud security is essential for safeguarding SaaS applications in an era of increasing cyber threats. Organizations can secure their applications, data, and users by understanding its principles, adopting best practices, and leveraging advanced tools. As technology evolves, staying ahead of future threats will ensure that SaaS environments remain secure and reliable.