Software-as-a-service (SaaS) solutions simplify how companies deliver applications, store data, and serve customers online. Instead of installing programs on local servers or individual devices, users access software hosted in the cloud. This approach offers cost savings, automatic updates, and flexible scaling.
Any service that processes client data must follow strict rules. Legal requirements, industry guidelines, and ethical standards outline how SaaS providers should manage, store, and transmit information. This process, called SaaS compliance, involves meeting specific regulations to maintain data safety, user confidence, and regulatory approval. Below, we explore why compliance is vital, the common frameworks, and how to keep cloud-based software lawful and secure.
Why SaaS Compliance Matters
Protecting Confidential Data
SaaS platforms often host financial records, personal information, or medical files. Mishandling these items or failing to shield them from cyberattacks can lead to identity theft, fraud, or significant reputational harm. Following well-known standards helps providers reduce these threats and show users that their data stays private and protected.
Data breaches also carry financial risks. Firms may pay steep fines, face lawsuits, or lose valuable customer relationships. For example, a platform that fails to encrypt credit card data might be accountable for fraudulent charges. By embedding security measures throughout the system, SaaS providers can lower these dangers and demonstrate proactive responsibility.
Boosting Client Confidence
Customers want reassurance about data security. Large enterprises and smaller companies alike seek confirmation that a SaaS platform is trustworthy. They need to know their files, internal messages, and sensitive transactions are not at risk. During customer onboarding, providing easy-to-read compliance summaries reassures new users that their sensitive data is handled responsibly. Meeting major regulations underscores professionalism and builds reliability.
Confidence goes beyond retaining current users, it attracts potential buyers. Prospective clients often review certificates or audit results before investing in a service. They treat these validations as proof of safer practices. In a busy market, a well-displayed commitment to compliance can set one SaaS product apart and encourage long-term brand loyalty.
Avoiding Fines and Lawsuits
Global regulations create strict rules for processing personal details. Violations may trigger investigations, costly penalties, or even forced shutdowns. A SaaS business based in Europe must adhere to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and a U.S. firm that handles patient data must address HIPAA standards.
Fines for ignoring these mandates can be harsh. GDPR penalties can reach millions of euros, especially for major breaches or repeated offenses. Even minor issues can disrupt services, consume resources in legal proceedings, and harm a company’s public image. Consistent adherence to regulations keeps your team focused on growth rather than legal recovery.
Common Compliance Frameworks for SaaS
GDPR
European Union introduced the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in 2018, and it has changed how organizations worldwide safeguard data. It applies to any entity handling personal information of EU residents, regardless of that entity’s location. Requirements span explicit data collection consent, careful storage, and quick reporting of breaches.
SaaS providers must comply if they have even one EU user. This entails building privacy by design from the start, auditing data flows frequently, and respecting user rights (for example, the right to request erasure). Non-compliance can result in fines of a maximum of 4% of yearly turnover or 20 million euros, whichever is greater.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
U.S. healthcare organizations and affiliated partners have to secure medical information under HIPAA. Any SaaS platform dealing with patient data is subject to HIPAA rules on access, encryption, and detailed audit logs.
Hospital billing systems, appointment schedulers, and telehealth services are prime examples. Medical entities typically require Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with SaaS providers to confirm compliance. Breaches can lead to civil fines, criminal charges, and loss of trust among healthcare providers and patients.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
Credit card networks created PCI DSS to safeguard cardholder details. SaaS platforms that store, process, or send payment info must meet these protocols, including network security, encryption, and frequent vulnerability checks.
This standard is vital for e-commerce tools, billing platforms, or any subscription-based service processing recurring fees. Though not a federal law, failing to comply can cause major fines from banks, higher transaction costs, and potential inability to handle credit card transactions. Customers also lose faith in services that fail to protect basic payment details.
Other Regional Rules
Beyond these major examples, many regions have their own regulations. Brazil’s LGPD covers data handling for Latin American users, while Canada’s PIPEDA sets expectations for personal info in Canadian provinces. Certain U.S. states, such as California with the CCPA, provide additional consumer protections.
A business with a global customer base must track these evolving requirements. Solutions that already follow GDPR may still need adjustments for other jurisdictions. Staying vigilant about regional changes avoids rushed code edits or hasty overhauls.
Steps to Achieve SaaS Compliance
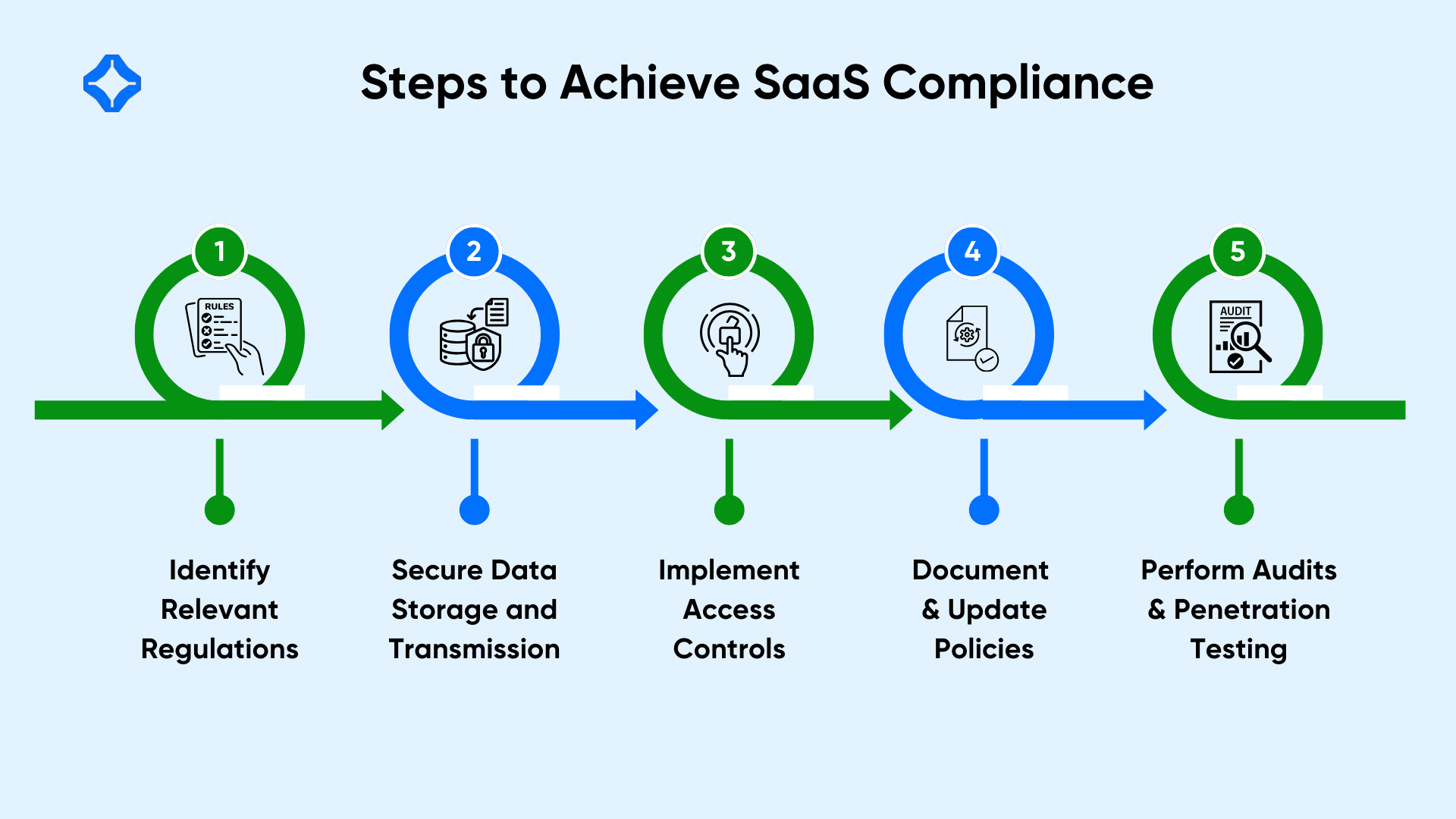
1. Identify Relevant Regulations
Start by studying your user base, the data types you handle, and your sector. A telehealth app focusing on rural clinics may need to follow HIPAA for U.S. patient data and GDPR for any European clients. An e-commerce billing tool might prioritize PCI DSS. Clarifying these obligations ensures the compliance roadmap stays manageable.
Many companies build a matrix listing data categories matched with specific rules. For example, “home addresses” align with GDPR’s data processing guidelines, and “medical lab results” link to HIPAA privacy rules. This document gives internal teams a single reference for areas of vulnerability.
2. Secure Data Storage and Transmission
Robust encryption is the foundation of data security. Data at rest saved in databases or backups usually uses AES-256 or similar algorithms. Data in transit moving across networks should rely on TLS (Transport Layer Security) or HTTPS.
Major cloud services include encryption key management, identity verification, and alert systems for suspicious activity. Even so, the SaaS provider remains responsible for safeguarding data at the application level. Carefully written code, continuous updates, and zero tolerance for insecure endpoints protect both the platform and its users.
3. Implement Access Controls
Not every employee or contractor needs full visibility of all data. Use role-based access or a more advanced approach, depending on the complexity of your system. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) can be enforced for privileged accounts.
Logging is equally important. Track when someone logs in, which records they view, and any changes they make. This data proves vital if investigating a breach or verifying compliance during audits. Suspicious patterns, such as excessive data exports or logins at odd hours, should trigger an immediate review.
4. Document and Update Policies
Guidelines inform employees how to manage user requests, store information, or handle possible security threats. These detailed procedures outline steps for everything from granting new staff access to dealing with a system outage.
Policies must evolve as new features launch, laws shift, or staff changes occur. Regular revisions, maybe quarterly, maintain consistency. During official audits, thorough documentation validates that your team enforces clear, consistent rules.
5. Perform Audits and Penetration Testing
Compliance is never static. As hackers refine their methods, your defenses must keep pace. Penetration tests simulate attacks to identify potential gaps, while vulnerability scans spot known software flaws.
Some SaaS providers hire outside consultants or security experts for unbiased inspections. These experts create detailed reports on any discovered issues and how to address them. By resolving flaws proactively, you reduce the chance of a severe incident that could spark fines or lawsuits.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Rapidly Changing Regulations
Regulatory landscapes evolve. New laws emerge with different definitions of personal data and new timelines for breach notifications. Ignoring these shifts may put you out of compliance unintentionally. Keeping an eye on legal updates, joining privacy-related groups, or working with specialized attorneys helps you stay ahead.
Agile methods let your team adjust quickly. If a new state law mandates data localization, a flexible architecture can place user info on servers in that region. By preparing for fluid regulations, you lower last-minute stress and avoid hasty patchwork fixes.
Balancing Security with Ease of Use
Too many security steps may frustrate users and push them to simpler competitors. Weak protection leaves you open to attacks. The best path encourages effective security without crushing the user experience.
Optional MFA for everyday accounts, combined with mandatory MFA for admin roles, is one possibility. Adaptive authentication can also be implemented. When a login attempt looks risky, the system adds layers of verification. This way, users navigate most tasks effortlessly while still blocking real threats.
Third-Party Integrations
SaaS rarely exists in isolation. Payment gateways, analytics tools, and external mailing services often connect to your platform. Each of these relationships might create new vulnerabilities if the partner’s security is weaker.
Before integrating, check a partner’s policies, certifications, and incident response track record. Regularly update your list of approved vendors and run security reviews. If a third party gets compromised, your customers will still hold you responsible for any data leak.
Detailed Look at Security Controls
Encryption
A strong encryption strategy involves several layers. Disk-level encryption keeps unauthorized individuals from accessing raw data if they physically seize a server. Tokenization can protect individual fields, such as credit card details. Even if someone manages to view the storage disk, the data remains jumbled.
Transport security relies on TLS 1.2 or newer versions. Websites employ HTTPS, guaranteeing that user information remains confidential in transit. Activating HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) forces browsers to use HTTPS, preventing attackers from stripping secure connections.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM solutions organize who can see or change different resources. Basic role-based access control (RBAC) assigns responsibilities based on job duties, while attribute-based access control (ABAC) can factor in user roles, location, or device type. This granularity raises protection levels.
Additionally, consistent user offboarding is essential. If someone leaves the company, their logins should be disabled immediately. Auditors often check if ex-employees can still log in, since this is a clear indicator of mismanaged access.
Security Incident Response
No system is immune to breaches. A thorough plan outlines which people to notify, how to isolate attacked servers, and how to restore from backups. Training exercises help staff respond quickly under real pressure.
Breach notification laws require prompt alerts to regulators and affected users, sometimes within hours. Delays can inflate penalties and worsen reputational harm. Coordinated communications with the press, shareholders, and clients to minimize confusion when an incident happens. Follow-up reports, including steps taken and lessons learned, help refine future defenses.
Helpful Tools and Certifications
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is a globally recognized benchmark for information security management. Organizations following ISO 27001 systematically handle risks, formalize processes, and track improvements over time.
SOC 2
This reporting standard examines how well a service provider meets key principles like security, availability, and confidentiality. An external auditor verifies that your controls are effectively implemented, resulting in a positive SOC 2 report.
Compliance Management Platforms
Software designed to streamline tasks such as policy enforcement, staff certification, and detailed audit trails. Many come with dashboards that highlight unaddressed areas, so the compliance team can prioritize fixes.
Long-Term Advantages of Strong SaaS Compliance
Competitive Standing
Having solid security is more than reducing the risk it can attract customers. Enterprises often prefer a platform with robust compliance features. Displaying credentials helps you stand out. This is especially true if competing services cut corners or have no recognized certifications.
Smooth Expansion
When data governance is part of your foundation, rolling out new tools or entering new regions is less chaotic. You are unlikely to fall foul of rules if your engineering, QA, and policy teams already champion best practices. This flexible approach helps you expand without rewriting major components.
Ongoing User Loyalty
Data breaches often dominate headlines, shaking confidence in the affected brand. In contrast, a clean record fosters loyalty from existing clients. They appreciate your investment in keeping their information safe. Positive testimonials and references often grow naturally when customers recognize a consistent commitment to data security.
Conclusion
SaaS compliance is more than a check-the-box activity. It underscores your promise to safeguard user information, uphold legal mandates, and maintain a stellar reputation. Whether you handle medical records, payment transactions, or personal data, the right combination of encryption, access limits, and documented procedures forms a strong backbone for secure cloud operations.
In a rapidly changing digital environment, preparedness matters. Identify which regulations apply, strengthen key security measures, and adjust as rules or technology evolve. This thinking sets your SaaS platform on solid ground and protects both your clients and your long-term success. By viewing compliance as an ongoing endeavor, you defend user data and support your brand’s future.
FAQs
SaaS compliance refers to following legal, regulatory, and industry-specific standards to ensure data security, privacy, and operational integrity in cloud-based software services.
Compliance protects customer data, builds trust, prevents legal penalties, and ensures smooth business operations by adhering to security and privacy regulations.
Important standards include GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2), HIPAA , ISO 27001 , and PCI-DSS.