AI agents in SaaS offer automated solutions for tasks like data analysis, customer support, and process control. They gather information, learn from it, and take actions that improve user outcomes. Modern businesses benefit from these agents to reduce costs and simplify workflows. By integrating AI agents into SaaS, organizations reduce manual effort and gain insights in real time.
Below, we explore how AI agents function, their benefits, and the steps involved in building them. We also cover the future of these tools and the challenges that may arise. With a practical roadmap, you can see why AI is reshaping SaaS applications.
Why Businesses Are Adopting AI Agents
Companies value AI for reducing time-consuming tasks. AI agents respond quickly to customer queries, analyze data, or recommend solutions. They also help teams discover new opportunities by sifting through large datasets. This proactive assistance improves efficiency and keeps users engaged.
Organizations want to be more competitive and responsive. By automating repetitive tasks, AI frees employees to handle higher-level efforts. This shift leads to leaner operations, stronger insights, and better outcomes.
What Are AI Agents?
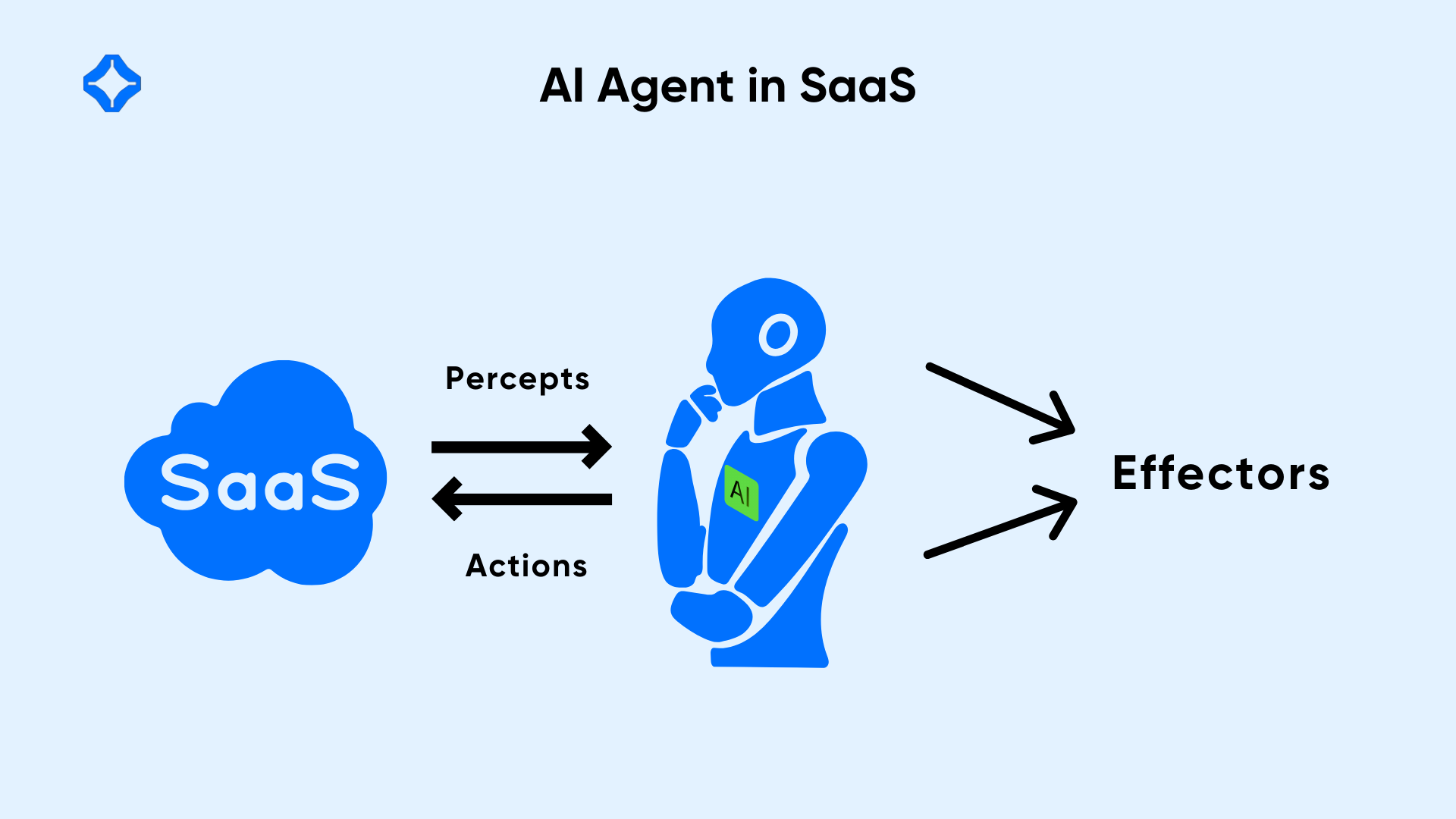
AI agents are programmed systems that make decisions or carry out tasks on behalf of users. They interpret data, recognize patterns, and adjust as new info arrives. They work in digital spaces, often linking various services to achieve real-time decisions.
Definition of AI Agents
These agents rely on rules or machine learning algorithms to process incoming signals. Rule-based agents follow predefined instructions. Machine-learning-based agents adapt using data and feedback. Both types can respond to prompts or initiate actions.
Types of AI Agents in SaaS
- Reactive AI Agents rely on fixed responses to inputs. They address events quickly but lack long-term learning.
- Proactive AI Agents predict likely outcomes and handle tasks based on past patterns. They can anticipate user needs.
- Autonomous AI Agents evolve continuously and make choices independently. They gain experience through repeated interactions.
How AI Agents Work in SaaS Platforms
AI agents depend on structured workflows that let them learn and respond effectively. They gather data, apply AI models, act on insights, and keep refining their methods. This cycle helps them evolve as their environment changes.
Step 1: Data Collection and Analysis
Agents understand user actions, databases, and external APIs to gather facts. They may parse text or numerical data, turning it into structured inputs. Quality data is essential for meaningful conclusions, so teams must ensure accuracy and consistency.
Unstructured data formats, like emails or social media posts, requires extra processing. Natural language processing helps transform text into a format AI agents can understand. Once processed, this data guides the agent’s next steps.
Step 2: AI Models and Decision-Making
Once the agent has input, it runs that data through models like machine learning or NLP. These algorithms identify patterns, classify information, or predict what might happen next. The agent’s logic then decides how to respond.
Predictive analytics spots emerging trends in the data. For example, machine learning SaaS solutions drive these AI models, extracting valuable insights from real-time data. The AI agent uses these predictions to recommend stock adjustments or marketing actions.
Step 3: Action Execution and Learning
After the agent decides on a course of action, it carries it out automatically. This might involve sending notifications, updating records, or performing tasks on external platforms. Throughout this process, the agent logs outcomes to predict success.
When something goes wrong, the agent gathers feedback to refine future actions. This learning loop is critical. Each interaction shapes how the agent reacts to similar situations. Over time, the AI agent grows smarter.
Step 4: Integration with SaaS Workflows
AI agents typically embed in SaaS platforms like CRMs or ERPs. They connect using APIs that enable quick data exchanges. Real-time inputs guide the agent’s decisions, letting it interact seamlessly with existing tools. This deep integration ensures the agent’s outputs align with normal workflows.
Because the AI agent operates in sync with SaaS processes, it can monitor key events and respond instantly. This centralized approach cuts manual tasks and keeps business data unified.
How to Build an AI Agent for SaaS
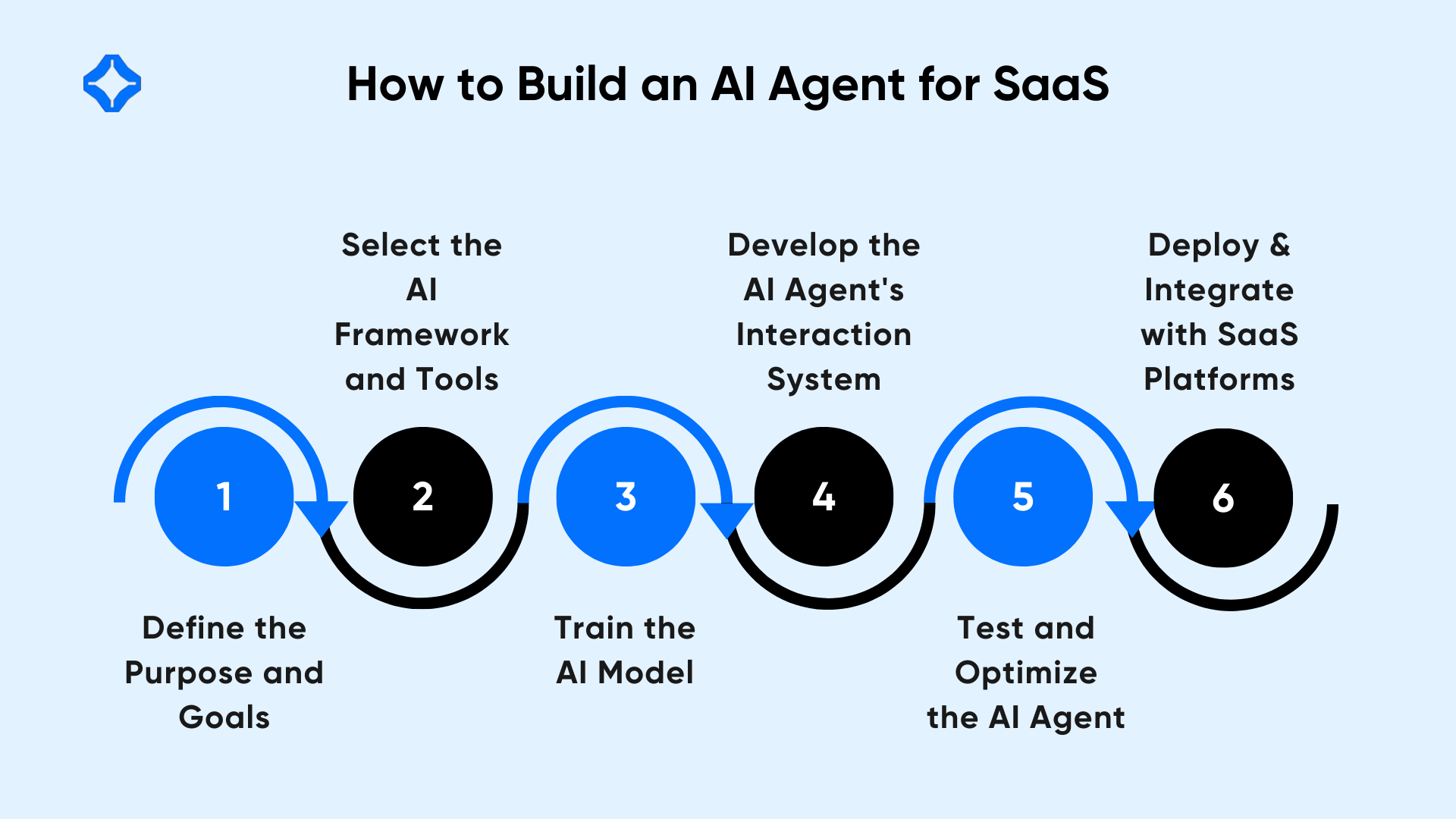
Creating an AI agent involves careful planning, model development, and smooth deployment. Below is a framework that helps teams move step by step.
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Goals
Decide what your agent should handle, like chat support or analyzing financial data. Clarify whether it needs reactive, proactive, or autonomous features. When the goal is clear, the team can focus on relevant data and tasks.
Step 2: Select the AI Framework and Tools
Some companies opt for pre-built services from providers like Google AI, AWS AI, or OpenAI. Others build custom solutions with frameworks such as TensorFlow or Scikit-learn. Low-code AI platforms can speed up deployment for teams without deep coding expertise.
Compare pricing, features, and ease of integration. Think about whether your use case demands advanced customization or if a managed service is enough. This decision shapes how much time and skill you need.
Step 3: Train the AI Model
Collect and prepare data that represents the tasks your agent will tackle. Clean it by removing duplicates or errors. Then, train a suitable machine learning or deep learning model. This might involve classification, regression, or reinforcement learning.
Reinforcement learning lets agents learn through trial-and-error rewards. The agent tests, moves, analyzes results, and refines future actions. This approach suits advanced scenarios with continuous feedback loops.
Step 4: Develop the AI Agent’s Interaction System
If your agent will talk with users, include NLP( Natural Language Processing). Tools like GPT or BERT parse language for more natural responses. For structured tasks, design the agent’s logic so it uses historical info and real-time signals to decide.
Maintain a blend of elegance and simplicity. Overly complex systems may confuse users or slow performance. Aim for an agent that is accurate yet easy to integrate with existing SaaS interfaces.
Step 5: Test and Optimize the AI Agent
Simulate real interactions to see how well your AI performs. Gather feedback from test users, then fine-tune model parameters or data sets. Keep measuring accuracy and response speed.
Track how often the agent’s recommendations match desired outcomes. If issues persist, retrain or adjust settings. A continuous improvement mindset helps maintain agent reliability.
Step 6: Deploy and Integrate with SaaS Platforms
Finally, merge your agent into the chosen SaaS environment. Configure security controls to guard sensitive data. Set up monitoring tools that track agent health and user satisfaction. Ensure the system can scale with higher loads.
APIs link the AI agent to various SaaS modules. Frequent checks ensure the smooth operation of these agents. If usage expands, your team might add computing resources or refine the model. A stable deployment with clear monitoring makes the system reliable.
Benefits of AI Agents in SaaS
An AI agent can be a game-changer when it is implemented correctly. It helps teams cut costs, improve speed, and manage data more productively. By automating routine work, AI agents also free employees from strategic tasks that spark innovation. This approach leads to smoother operations and stronger results in fast-paced environments.
Increased Automation
Businesses automate tasks like data entry, form processing, or report generation. This lowers manual workload and eliminates human errors. They also maintain 24/7 efficiency, reducing delays linked to human schedules.
Implementing workflow automation further accelerates these routine processes, allowing AI agents to manage day-to-day tasks with minimal human intervention. By removing repetitive tasks, AI agents enable staff to focus on creative problem-solving.
Improved Decision-Making
Agents examine user behavior, market trends, or operational metrics. They then deliver insights that guide managers or trigger automated actions. They recognize subtle patterns humans might overlook, allowing for timely and precise decisions. This data-driven approach helps teams respond quickly to market shifts.
Cost Savings
With fewer manual tasks, companies see lower staffing expenses in certain areas. Automated operations also cut the chance of expensive mistakes. This resource efficiency lets firms invest more in research and development. Scaling back on overhead costs boosts overall profitability in the long run.
Scalability
AI agents can handle large user bases or heavy data loads with minimal slowdown. When demand grows, cloud infrastructures can scale on demand. Businesses maintain consistent service quality despite surges in traffic. A stable, flexible platform increases user satisfaction and sustained growth.
Real-World Applications of AI Agents in SaaS
AI agents already serve in many sectors. Below are some common use cases that show their range and value. Their ability to automate tasks and learn from data empowers companies to excel in crowded markets. By handling routine tasks, these agents free team members to focus on strategic decisions.
AI Chatbots for Customer Support
They answer basic questions, handle returns, or create support tickets. Advanced bots interpret user intent and direct complex issues to human agents. They work around the clock, boosting availability for shoppers in different time zones. By resolving routine tickets, chatbots reduce wait times and raise overall satisfaction.
AI-Powered Data Analysis
Agents scrape metrics, recognize trends, and generate forecasts. Analysts can then verify the results to shape strategic moves or plan expansions. They detect anomalies in real time, preventing errors from piling up. By revealing emerging patterns early, teams gain a sharper view of market shifts.
AI Agents in Marketing Automation
These agents craft personalized messages or place ads based on user habits. Leads receive customized attention, raising engagement and conversions. They also track user interactions and fine-tune campaigns for maximum impact. By focusing on relevant prospects, marketers save resources and boost return on investment.
AI in IT Management
They watch system performance, detect outages, and self-correct certain errors. This cuts downtime and saves teams from constant manual monitoring. Automated alerts let IT staff tackle potential issues before they grow serious. Continuous oversight improves system reliability for both employees and end users.
Challenges in AI Agent Development for SaaS
While AI agents bring many benefits, teams must address hurdles like data security and fair outcomes. Planning for these challenges keeps deployments on track.
Data Privacy and Compliance Issues
Strict rules govern how companies handle personal data. AI agents require clear protocols to prevent unauthorized access or breaches. Compliance with GDPR or CCPA protocols is essential.
Integration Complexity
SaaS ecosystems are usually very large. Merging an AI agent with multiple apps or legacy systems can be tricky. Thorough testing is essential to ensure smooth workflows.
Bias in AI Decision-Making
If training data is skewed, the agent may make unjust or inaccurate calls. Carefully filter training sets and set guidelines for fairness. Conduct audits to detect unintended bias.
The Future of AI Agents in SaaS
AI agents are becoming more powerful. Emerging features indicate they’ll play a greater role in SaaS, delivering complex services with minimal human supervision.
AI Agents Becoming More Autonomous
Some will handle bigger processes, like supply chain logistics or financial audits. They’ll keep learning and adapt to changes without direct human control.
Voice-Enabled AI Assistants in SaaS
As voice recognition advances, AI assistants may accept verbal commands to create reports or schedule tasks. This hands-free feature can boost productivity.
AI plus IoT in SaaS
AI agents could connect smart devices, gather sensor info, and make instant decisions. This synergy helps manage industrial equipment, retail stock, or building systems. For deeper insights into connected device management, explore IoT-enabled SaaS and discover how AI agents coordinate real-time data from sensors.
Conclusion
AI agents offer powerful advantages for SaaS. They automate key tasks, analyze data, and provide quick answers to user needs. As they grow smarter, businesses cut costs and refine processes.
Adopting AI agents starts with defining clear goals and choosing the right tools. Data quality and security must be a priority. With careful planning, companies can unlock new levels of efficiency. The path ahead points to increasingly autonomous AI agents ready to handle complex workloads within SaaS frameworks.
FAQs
AI agents are programmed systems that make decisions or carry out tasks on behalf of users. They interpret data, recognize patterns, and adjust as new info arrives. They work in digital spaces, often linking various services to achieve real-time decisions.
AI agents can be classified into reactive agents, proactive agents and autonomous agents. They range from simple rule-based systems to advanced AI that adapts based on experience.
Businesses use AI agents for customer support (chatbots), data analysis, process automation, cybersecurity, and decision-making. They improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences.
Industries such as healthcare, finance, e-commerce, manufacturing, and marketing leverage AI agents for automation, predictive analytics, and personalized services.