Automation is revolutionizing financial management processes, helping businesses streamline operations, reduce errors, and make informed decisions faster. By integrating advanced tools and technologies, organizations can optimize workflows and shift focus toward strategic growth.
This article examines how automation is reshaping financial management, best practices for financial automation, and the challenges businesses encounter during adoption.
The Evolution of Automation in Finance Management
Automation in finance has evolved significantly over the years, moving from basic calculators to AI-powered solutions. Early financial tools focused on simplifying manual tasks like bookkeeping, while modern automation platforms handle complex processes such as predictive analytics and real-time reporting.
This progression allows businesses to manage finances more efficiently and adapt to changing demands in a competitive environment.
Understanding Automation in Business Finance
Automation in business finance uses technology to handle routine tasks like accounting, payroll, invoicing, and tax compliance. These processes save time and reduce errors, ensuring smoother financial operations.
Automation provides consistency by processing data uniformly across financial operations. Payroll systems, for instance, automate salary calculations and payments, eliminating manual mistakes. Invoicing tools also streamline billing and payment tracking with minimal oversight.
Automation also enables financial teams to focus on strategy by reducing the burden of repetitive work. Relieved of manual tasks, teams can dedicate more time to forecasting, resource planning, and decision-making, driving long-term growth.
Key Areas of Finance Management Impacted by Automation
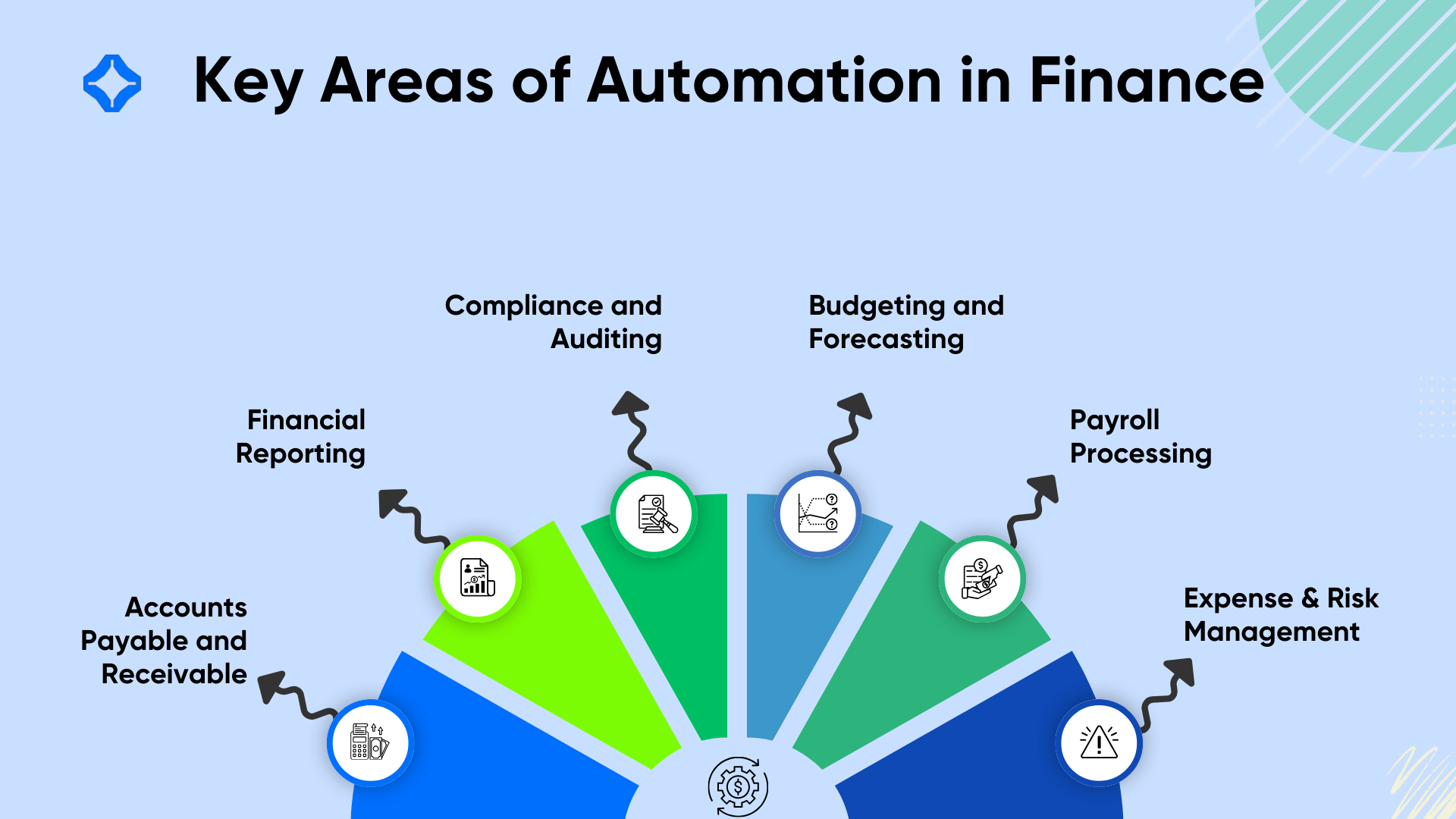
Accounts Payable and Receivable
Automation has revolutionized the handling of accounts payable and receivable, making these processes faster and more accurate. Automated systems streamline invoice processing by capturing data from invoices, validating them against purchase orders, and flagging discrepancies.
Payments are scheduled automatically, reducing delays and avoiding penalties for late transactions. For accounts receivable, automation helps track outstanding invoices, send reminders, and improve cash flow by Speeding up collections. These systems minimize manual effort while ensuring timely and error-free transactions.
Financial Reporting
Generating financial reports manually is time-consuming and prone to errors, but automation solves these challenges effectively. Automated reporting tools compile data in real-time, offering insights into cash flow, profitability, and operational expenses at a glance.
Businesses can customize reports to focus on specific metrics or trends, enabling better decision-making. With real-time access to data, financial teams can quickly adapt to changing conditions and provide stakeholders with accurate and timely updates.
Compliance and Auditing
Maintaining compliance with financial regulations is essential for businesses, and automation simplifies this process.
Automated systems track transactions, store documentation securely, and generate detailed audit trails. These tools ensure that businesses remain compliant with laws like GDPR, SOX, or tax regulations, minimizing the risk of penalties.
Automation minimizes human error and offers a clear view of financial activities, making audits faster and less complicated.
Budgeting and Forecasting
Automation significantly improves budgeting and forecasting processes by analyzing historical data and predicting future trends. These tools generate accurate forecasts that help businesses allocate resources effectively and prepare for market changes.
Automation uses real-time data to offer dynamic budgeting capabilities, enabling organizations to adapt their plans to evolving conditions.
Expense Management
Automated expense management systems streamline the process of tracking and reimbursing employee expenses. These platforms automatically categorize expenses, flag policy violations, and generate detailed reports.
Reducing manual intervention helps businesses maintain compliance with internal policies while saving time and effort.
Payroll Processing
Payroll is another area where automation has made a significant impact. Automated payroll systems handle tasks such as calculating salaries, deducting taxes, and processing payments with precision. These tools also generate payslips and maintain compliance with tax regulations, reducing administrative workload and errors.
Risk Management
Automation tools help identify and mitigate financial risks by analyzing data and spotting irregularities. Fraud detection systems, for example, monitor transactions for unusual patterns, flagging potential threats in real-time.
Benefits of Automation in Financial Processes
Increased Efficiency
Automation accelerates routine financial tasks, cutting down the time spent on repetitive tasks. Streamlined processes enable teams to focus on initiatives that drive growth and contribute value to the organization.
Reduced Errors
Financial automation ensures accuracy by following structured workflows and minimizing common mistakes in data entry or calculations. This precision helps maintain error-free records and smooth day-to-day operations.
Cost Savings
By simplifying complex workflows, automation lowers operational costs by reducing reliance on manual efforts. This efficiency allows businesses to allocate budgets more effectively toward other priorities.
Real-Time Insights
Automated tools deliver up-to-date financial information, helping businesses quickly assess their cash flow and revenue trends. This clarity supports better decision-making and keeps organizations adaptable to market changes.
Improved Compliance
Automation ensures compliance by standardizing processes and maintaining accurate records for audits. Automated systems simplify tax filing and other regulatory tasks, making adherence to laws more manageable.
Enhanced Scalability
Automated systems grow effortlessly alongside businesses, managing increased workloads and complex tasks. This adaptability makes it easier for companies to expand operations without major adjustments.
Tools and Technologies Driving Financial Automation

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
ERP systems consolidate financial data into a single platform, simplifying the management of budgets, expense tracking, and performance analysis. These systems help businesses maintain consistency across departments, offering a unified view of financial operations and enhancing decision-making capabilities.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA technology takes over repetitive tasks like invoice management, account balancing, and manual data input. By handling these activities quickly and accurately, RPA enhances efficiency in operations, enabling teams to dedicate their time to more valuable tasks.
Cloud-Based Financial Platforms
Cloud financial solutions offer secure, on-demand access to tools, cloud security and data from anywhere. They facilitate real-time collaboration among teams and allow businesses to scale operations without significant infrastructure investments.
Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
BI tools collect and process financial data to produce clear visual reports and actionable insights. They enable organizations to monitor performance, identify trends, and improve financial planning for better results.
Automated Tax Compliance Software
Tax compliance software automates essential tasks such as calculating liabilities, preparing returns, and creating detailed compliance reports. This softwares minimizes errors and helps businesses stay aligned with regulatory requirements.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain enhances financial automation by ensuring secure and transparent transaction processing. It reduces fraud risks, streamlines payment systems, and simplifies auditing through unmodifiable records. Businesses can rely on blockchain to build trust in financial transactions.
Expense Management Platforms
Automated expense management tools track and categorize business expenses in real-time, simplifying approvals and reimbursements. These platforms provide detailed reports that help businesses control spending and maintain financial discipline.
How AI and Machine Learning Are Shaping Finance Management
AI and machine learning transform finance management by enabling smarter automation and advanced decision-making. Predictive analytics powered by these technologies help businesses forecast trends, optimize budgets, and plan more effectively.
AI-powered chatbots streamline communication by handling customer inquiries and automating repetitive support tasks. This improves customer satisfaction and frees time for financial teams to focus on strategic goals.
Challenges in Adopting Finance Automation
Resistance to Change
Introducing automation often faces pushback from employees due to concerns about job security or discomfort with unfamiliar technology. Organizations need to address these fears by offering training and highlighting how automation supports, rather than replaces, their roles.
Initial Implementation Costs
The upfront expense of acquiring and implementing automation tools can hinder smaller businesses from adopting them. Thorough planning, gradual implementation, and considering cost-effective options can ease the financial strain of adopting automation.
Data Security Concerns
Automating financial processes requires integrating tools that handle sensitive data, making security a top priority. Implementing strong encryption, access controls, and compliance measures helps protect against breaches and builds trust in automated systems.
Lack of Technical Expertise
Some businesses struggle with adopting automation due to limited knowledge or experience with advanced tools. Partnering with experts or investing in training ensures smoother integration and more effective use of automation technologies.
Integration Challenges
Automating finance systems often involves integrating new tools with existing software, which can be complex. Incompatibility between systems or a lack of proper support can lead to inefficiencies, requiring businesses to plan integrations carefully.
Limited Scalability in Legacy Systems
Organizations using outdated financial systems may face difficulties scaling automation solutions. Modernizing infrastructure or adopting cloud-based tools can help overcome these limitations and improve flexibility.
Best Practices for Implementing Finance Automation
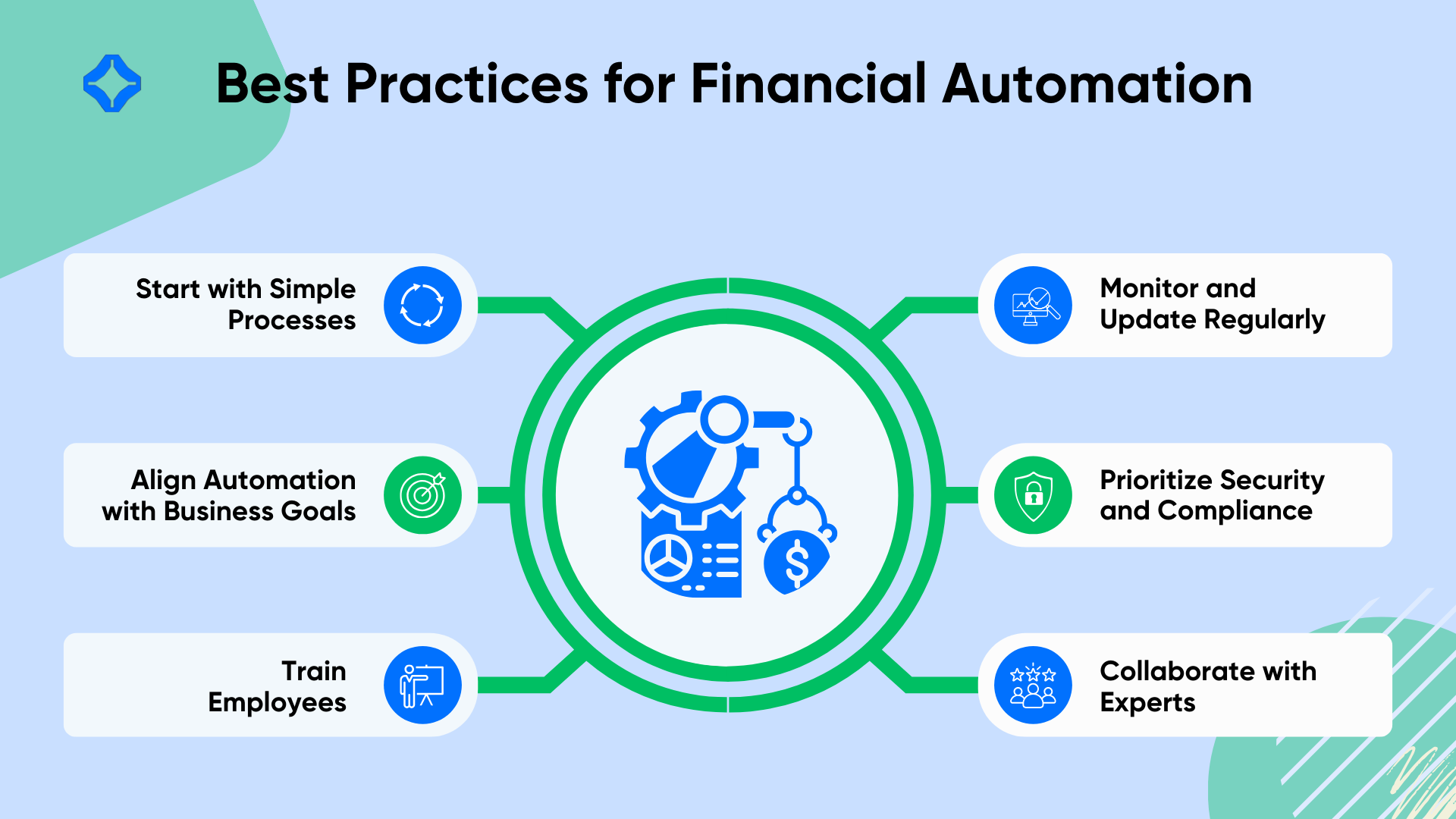
Start with Simple Processes
Focus on automating straightforward tasks like invoicing or payroll before advancing to more complex systems. This phased approach ensures smoother transitions and reduces risks.
Train Employees Thoroughly
Train your team with the necessary knowledge and skills to operate automation tools efficiently. Providing clear training promotes confidence and improves adoption rates.
Align Automation with Business Goals
Select tools that align with your organization’s objectives, ensuring that automation supports your broader financial strategy.
Monitor and Update Regularly
Regularly review automation systems to ensure they remain efficient and compatible with evolving technologies and business needs.
Prioritize Security and Compliance
Adopt security protocols to safeguard sensitive information and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. Secure systems build trust and reduce vulnerabilities.
Collaborate with Experts
Work with automation specialists or consultants to ensure proper implementation and integration with existing systems. Expert guidance minimizes errors and maximizes results.
Conclusion
Automation is reshaping financial management, empowering businesses to streamline operations, lower expenses, and make informed decisions. Leveraging advanced tools allows organizations to address challenges effectively while opening doors to new growth opportunities. As technology progresses, automation will remain vital to financial strategies, driving efficiency and long-term success.